
AI might crack over 50% of password in less than a minute: Study


An Artificial Intelligence (AI)-assisted tool can crack over 50% of the most commonly used passwords in less than a minute, a new study published on Sunday said.
The study done by Melbourne-based Home Security Heroes, a group of online security experts, employed an AI password cracking tool called PassGAN (password generative adversarial network) to analyse a list of over 15 million passwords and also found that PassGAN can generate "multiple password properties and improve the quality of predicted passwords, making it easier for cybercriminals to crack your passwords and gain access to your personal data", the company said in the report. 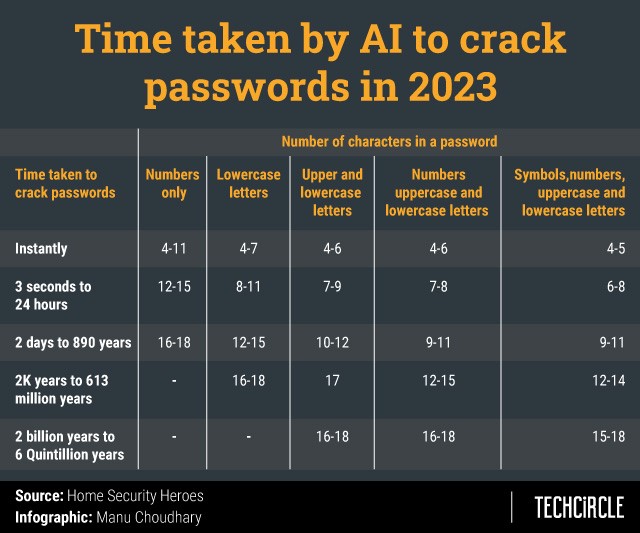
According to the study, 51% of common passwords can be cracked in under a minute, 65% in under an hour, 71% in under a day, and 81% in under a month. The research further showed that the majority of six-character passwords (or lesser) were cracked almost instantly. The study suggests that passwords with at least 18 characters are considered safe against tools like PassGAN, with a minimum of ten months required to crack an 18-character password containing only numbers.

Another recent report by cyber security firm Hive published on March 7 found that an 8-character complex password could be cracked in just 39 minutes if the attacker were to take advantage of the latest graphics processing technology. A seven-character complex password could be cracked in 31 seconds, while one with six or fewer characters could be cracked instantly. Shorter passwords with only one- or two-character types, such as only numbers or lowercase letters, or only numbers and letters, would take just minutes to crack.
According to Hive researchers, by renting computer and graphics hardware through Amazon AWS and other cloud providers, a cybercriminal can tap into multiple virtual instances of a powerful GPU to perform the password cracking at a fairly low cost. Due to the progress in graphics technology, most types of passwords require less time to crack than they did just two years ago. For example, a 7-character password with letters, numbers and symbols would take 7 minutes to crack in 2020 but just 31 seconds in 2022.
The latest report also points to brute force attack that involves 'guessing' username and passwords to gain unauthorised access to a system. A study published by cyber risk management firm Outpost24 research note in its report published in January 2023 that brute force attacks were the most repeated attack type in 2022 with 73,860 total number of attacking IPs.

These are not new attack techniques. But with the advent of generative AI tools such as Microsoft-backed Open AI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard making significant strides in transforming our lives, researchers believe AI's dark side is raising concerns, particularly when it comes to password cracking.
The Home Security Heroes researchers recommend businesses and end-consumers that as AI technology continues to advance it is important to use alpha-numeric passwords with at least 15 characters. That means, the password should have at least two letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoiding predictable patterns (e.g., “1234”) and regularly changing your passwords is crucial. Additionally, refrain from using the same password across multiple accounts.
The researchers also said that to help you remember complex passwords, consider using a password manager. As AI technology progresses, it’s essential to stay one step ahead of potential threats and ensure the security of your online accounts.

Last month, Microsoft brought attention to the security concerns that will come with the quick advancement of AI by announcing its new Security Copilot suite that will help security researchers protect against malicious use of modern technology.
Meanwhile, cyber-crime is growing exponentially. According to Cybersecurity Ventures report published in December 2022 noted that the cost of cybercrime is predicted to hit $8 trillion in 2023 and will grow to $10.5 trillion by 2025.
