
Indian cos saw over 25% jump in cyber threats since the start of lockdown: Cisco


When India went into a lockdown in late March, companies across sectors looked for ways to maintain business continuity. Six months later, the threat landscape has seen a dramatic change, with home-based wifi connections exposing corporate data to cybercriminals.
About 73% Indian businesses experienced more than 25% jump in cyber threats and alerts since the start of COVID 19, according to the future of secure remote work report by networking major Cisco.
While organisations are increasingly looking at shifting to a hybrid future of work as many have already given up office spaces in the past few months, around 84% Indian organisations feel ensuring cyber security will be the top priority, especially information technology (IT) firms. In fact, within the ongoing months of remote working, 65% adopted cyber security measures. The study highlights that 77% of organisations in the region plan to increase their future investment in cybersecurity due to COVID-19.

“The pandemic has amplified the criticality of cybersecurity and brought new complexities to the fore. Now, as remote work continues to garner traction, organisations are turning their attention to building a robust cybersecurity foundation, with cloud security emerging as the top investment for 31% of companies in reinventing their workplaces post COVID-19," Vishak Raman, director, security business, Cisco India and SAARC said in a statement.
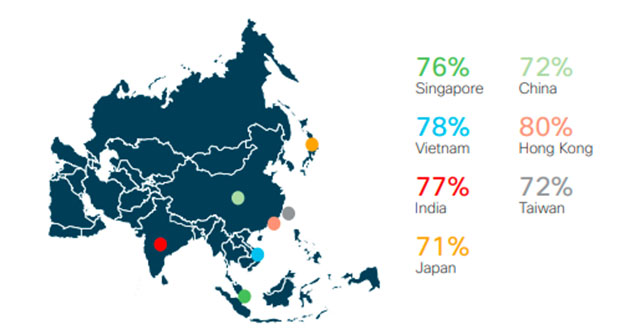
More than half of the APJC countries surveyed (Singapore, Vietnam, India, Japan, China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan) had over 70% of organizations indicating possible increases in cybersecurity investments, higher than the regional average

Protecting the endpoints have been a growing challenge for companies as users connect from their home Wi-Fi or use their personal devices to connect to corporate applications. About two in three respondents stated that office laptops/desktops (66%) and personal devices (58%) posed a challenge to protect in a remote environment, followed by cloud applications at 42%.
Although an estimated 95% of the companies globally have made changes in their cybersecurity policies and practices, the challenge remains to further simplify them and educate the employees. Almost 60% of Indian organizations said that having too many tools/solutions to manage was a challenge faced in reinforcing cybersecurity protocols for remote working, followed by a lack of employee education and awareness (55%).
Of the 95%, the top cybersecurity policy change made is to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) (66%), increase VPN capacity (62%) and increase web controls and acceptable use policy (62%). A focus on cloud security was the top ranked investment in terms of importance in preparing for a post COVID-19 workplace (31% ranked it first). Other priority investments reported by organizations include, overall cybersecurity defense posture (25% ranked first) and network access (25% ranked first).

Now around 53% of the companies in India expect more than half of their workforce to operate remotely post-pandemic. This is a major shift from only 28% of companies having more than half of their workforces working remotely pre-pandemic.
The study is based on a survey of over 3,000 IT decision-makers globally, of which over 1,900 respondents were from across 13 Asia Pacific markets, including India. Commissioned by Cisco and conducted by YouGov, the report explored the readiness of organisations globally, from small businesses to large enterprises, for the sudden transition to remote work, the challenges they faced, and how they are adapting their cybersecurity programs to enable hybrid work environments going forward.
